How Ethical Cashmere Sourcing Works in Nepal
In a world where sustainability and conscious consumerism are no longer optional, ethical cashmere has emerged as a powerful response to the environmental and social concerns linked to fast fashion. At the heart of this movement is Nepal, where tradition, skilled craft, and respect for nature create truly authentic, sustainable cashmere.
Understanding Ethical Cashmere
Ethical cashmere refers to the responsible and humane production of cashmere wool, with a focus on minimizing harm to animals, supporting fair labor practices, and reducing environmental impact. Conventional cashmere often involves labor exploitation and land overgrazing. Ethical sourcing prioritizes long-term well-being for both people and the planet.
This approach doesn’t just value the end product—it respects every step of the process, from how the goats are raised to how the garments are crafted. The result? Luxury products that consumers can feel genuinely good about wearing.
Core Values Behind Ethical Cashmere Production
There are three foundational principles behind ethical cashmere sourcing: animal welfare, human dignity, and ecological responsibility.
First and foremost, goats are treated with care and compassion. Instead of shearing, which can be stressful for animals, ethical producers opt for hand-combing, a gentler process aligned with the natural molting season.
On the human side, ethical sourcing ensures that workers involved in cashmere manufacturing in Nepal are paid fair wages, work in safe conditions, and are often part of family-owned or community-driven cooperatives.
Environmentally, sustainable practices such as rotational grazing, minimal chemical use, and traditional hand-weaving techniques help lower the carbon footprint and promote long-term ecological balance.
Why Nepal is a Hub for Sustainable Cashmere
Nepal’s unique geography and cultural heritage make it an ideal location for sustainable cashmere production. Nestled against the backdrop of the Himalayas, the country offers an ideal habitat for the Pashmina goat, whose soft undercoat yields world-renowned cashmere fibers.
But it’s not just about the raw material. Nepal has a rich legacy of weaving and textile art that stretches back centuries. This deep-rooted tradition continues today through small workshops and artisan collectives, many of which are led by women and indigenous communities. These artisans are not only masters of their craft—they’re stewards of ethical and sustainable fashion.
Indigenous Communities and Their Role
Local herders and craftspeople are central to the success of ethical cashmere in Nepal. These communities deeply understand the land, animals, and time-honored methods passed down over generations. Their involvement ensures that the production process remains aligned with cultural integrity and ecological balance.
By supporting these communities through direct trade and partnerships, ethical cashmere brands contribute to the preservation of heritage while fostering economic empowerment in rural regions.
Preservation of Traditional Techniques
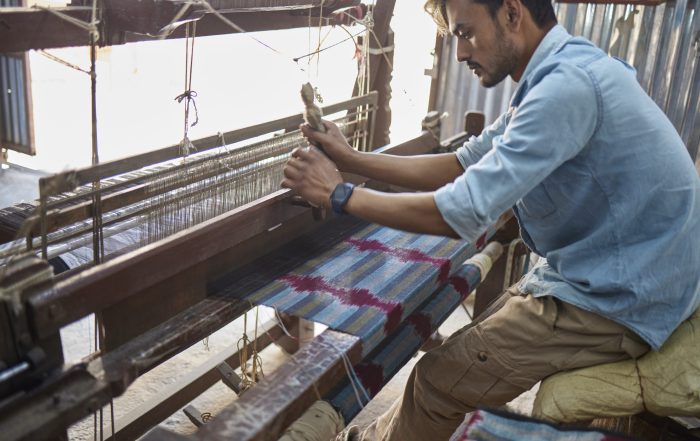
Unlike large-scale factories that rely on industrial processes, many Nepalese producers still use hand-spinning and hand-weaving techniques. They consume less energy, create little waste, and produce uniquely soft, character-rich cashmere.
Moreover, these old techniques ensure that the craftsmanship remains at the heart of the product—each piece is a reflection of the artisan’s skill, patience, and cultural identity.
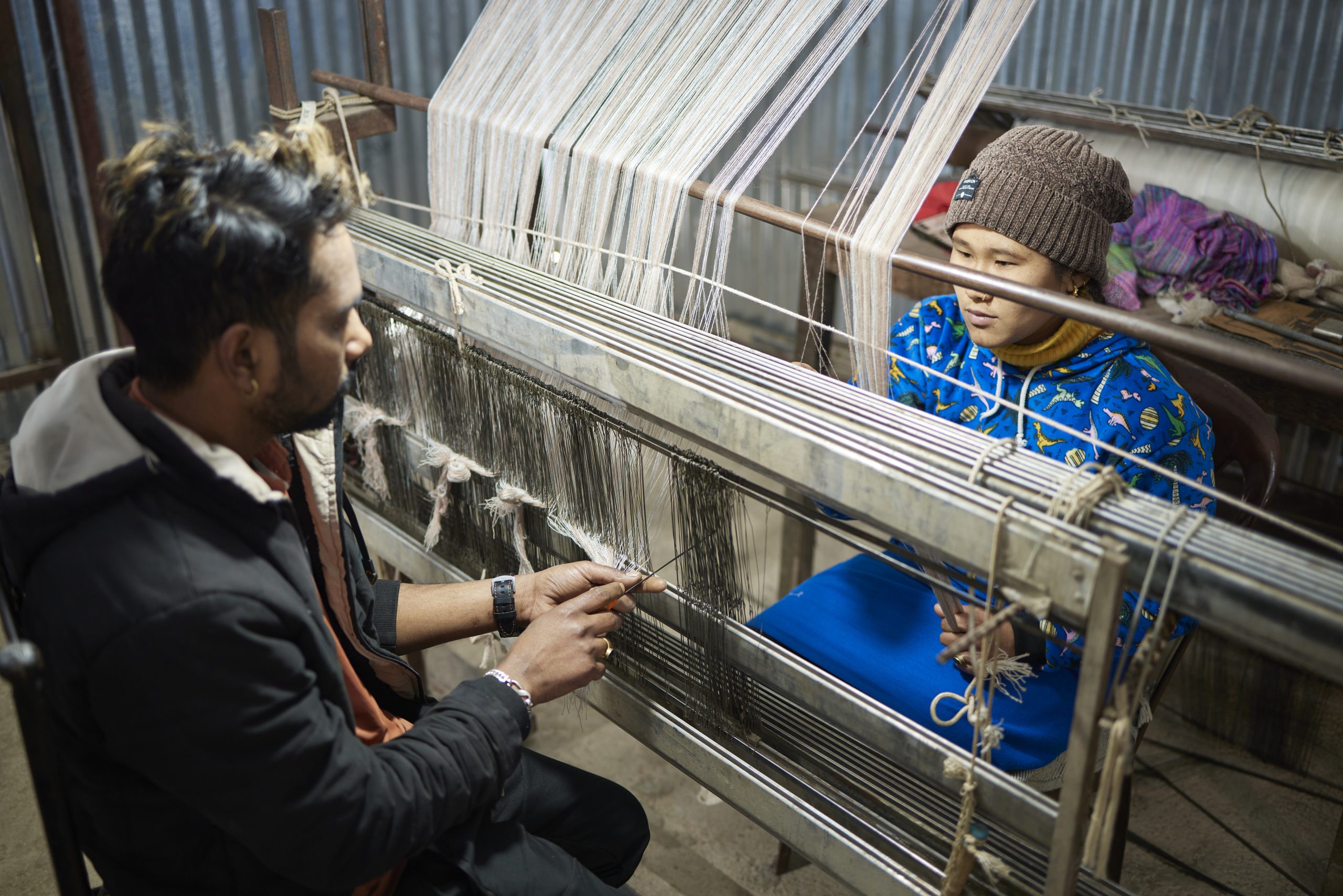
The Cashmere Manufacturing Process in Nepal
The journey of ethical cashmere in Nepal begins high in the Himalayas, where goats are combed during their natural shedding season. This ensures that the animals are not harmed or stressed in the process.
Once collected, the raw fibers are sorted and cleaned by hand. After cleaning, the cashmere is hand-spun into yarn—a slow but careful process that maintains the fiber’s quality.
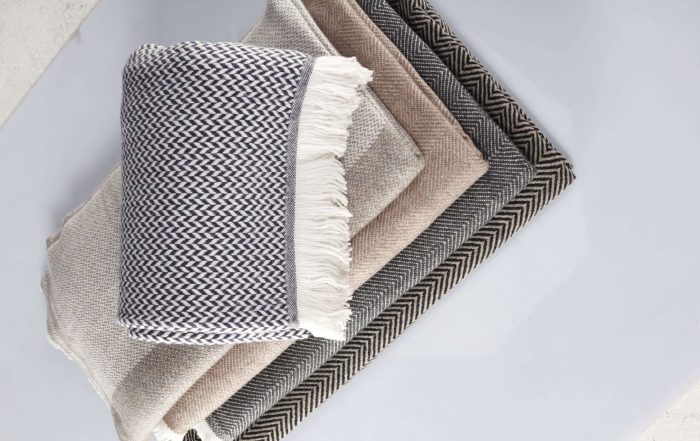
From there, skilled weavers transform the yarn into luxurious scarves, wraps, sweaters, and more. Many producers opt for natural or low-impact dyes, further reducing their environmental footprint.
Transparency and Traceability in Ethical Cashmere
One of the most critical aspects of ethical cashmere is the ability to trace the product back to its source. In Nepal, brands now adopt transparent supply chains, enabling customers to trace cashmere from herders to artisans.
GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) and Fair Trade certifications validate ethics while strengthening consumer trust.
Environmental Benefits of Sustainable Cashmere
When sourced ethically, cashmere becomes a truly sustainable fabric. It biodegrades naturally, requires less washing than synthetic fibers, and lasts for years with proper care.
Moreover, Rotational grazing and hand-processing help ethical cashmere protect soil, reduce water pollution, and lower energy use.
In a world where fast fashion dominates, investing in a durable, ethically sourced cashmere garment is a powerful act of environmental stewardship.
Challenges Faced by Ethical Cashmere Producers
Despite the growing interest in ethical fashion, challenges remain. Infrastructure in rural Nepal can be limited, making transportation and communication difficult. Ethical practices raise costs, making competition with cheap mass-produced goods harder.
Still, the dedication of Nepalese artisans and ethical brands has helped the industry grow steadily, proving that quality and conscience can indeed go hand-in-hand.
The Role of Brands Like Everest Cashmere
Everest Cashmere exemplifies what it means to champion ethical cashmere. The brand supports local herders and artisans, prioritizing transparency, sustainability, and community
By partnering with rural cooperatives and investing in eco-innovation, Everest Cashmere makes sure each piece supports a greater purpose.
Partnerships with Local Communities
One of the most impactful aspects of Everest Cashmere’s model is its direct collaboration with the communities it sources from. By offering above-market wages, skills training, and reinvestment into local infrastructure, the brand not only produces beautiful products—it builds resilient economies.
These partnerships foster trust, dignity, and pride among workers, ensuring that ethical sourcing is not just a buzzword but a lived reality.
How Consumers Can Support Ethical Cashmere
Supporting ethical cashmere begins with informed choices. Look for brands that prioritize transparency, source from known cooperatives, and offer details about their manufacturing process.
Invest in fewer, higher-quality items, and take good care of them. Gentle washing, proper storage, and mindful use can extend the life of your garments, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Avoiding Greenwashing
Unfortunately, as ethical fashion gains popularity, so does greenwashing—the practice of making misleading sustainability claims. To avoid it, read product labels carefully, research brand values, and seek out third-party certifications whenever possible.
If a brand is vague about its supply chain or offers too-good-to-be-true pricing, it might not be truly ethical.
The Future of Cashmere Manufacturing in Nepal
The future of cashmere manufacturing in Nepal is bright. As global consumers demand more accountability and sustainability, Nepalese artisans and ethical brands are well-positioned to meet that need.
Better tech, stronger infrastructure, and global awareness give ethical cashmere the power to reshape luxury fashion for the future.
Final Thoughts on Ethical Cashmere Sourcing in Nepal
From Himalayan peaks to Nepalese weavers’ hands, ethical cashmere tells a story of care, tradition, and responsibility. In choosing pieces crafted with integrity, consumers not only enjoy unparalleled softness and elegance—they become part of a global movement toward a more sustainable and compassionate world